Heart attacks and strokes are two of the leading causes of death globally, yet many people confuse them or fail to understand their differences. While both are cardiovascular events that involve a sudden disruption of blood flow, they affect different organs and have unique causes and risk factors. This article provides a medically accurate, research-backed comparison of the major causes of heart attacks and strokes, along with practical prevention strategies.
Table of Contents
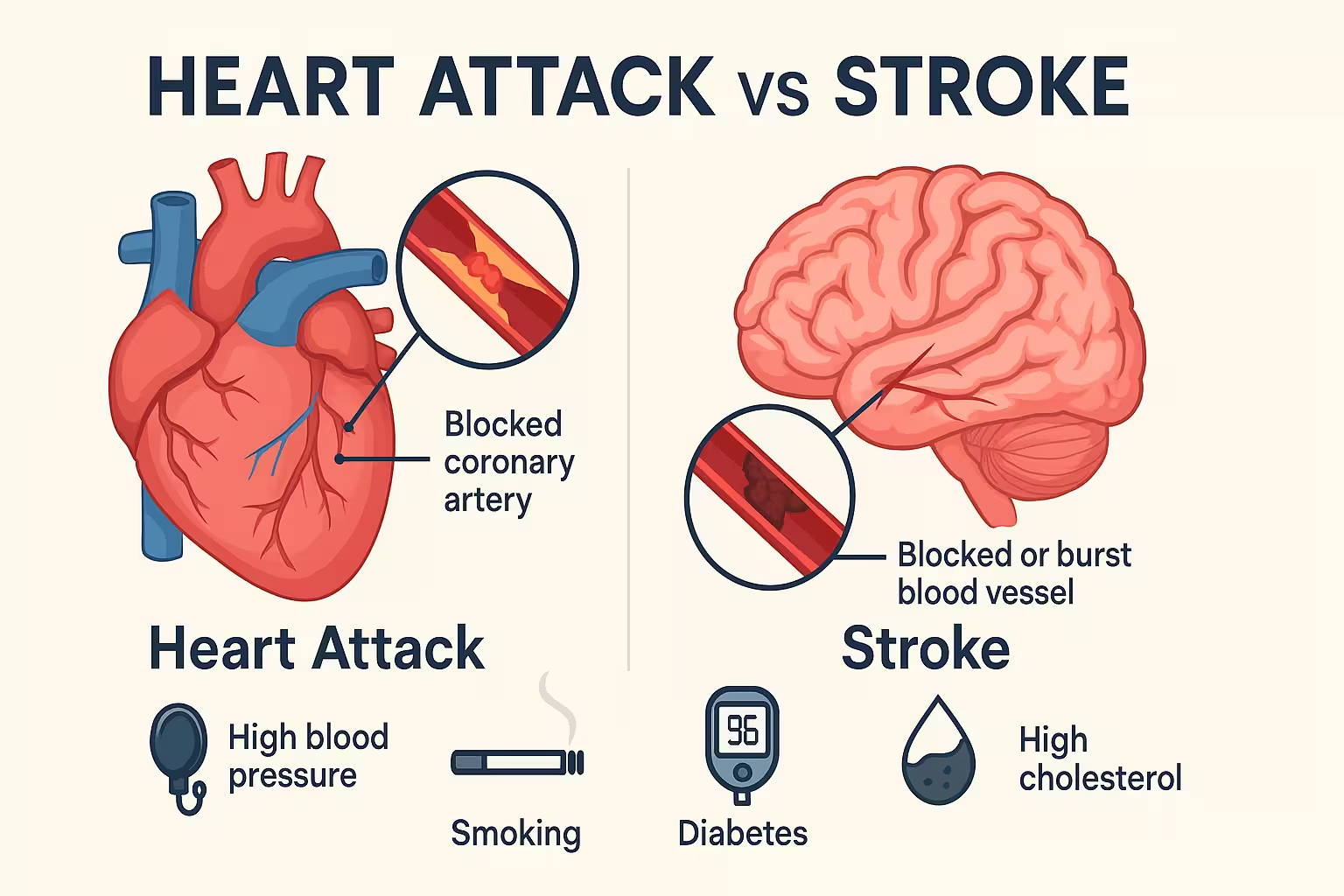
What Is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked. This blockage is usually caused by a build-up of plaque (a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other substances) in the coronary arteries. When the plaque ruptures, it can form a clot that blocks blood flow, causing damage to the heart muscle.
Read Also: Indian Air Force Medical Assistant Recruitment 2025 – Complete Details for Intake 02/2026
Major Causes of Heart Attacks:
- Atherosclerosis: The most common cause. This is the narrowing or hardening of arteries due to plaque buildup.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Puts strain on the heart and damages arteries.
- High Cholesterol: Especially LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, which contributes to plaque formation.
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and increases clotting risk.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar damages blood vessels over time.
- Obesity and Physical Inactivity: Linked to hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
What Is a Stroke?
A stroke occurs when blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. There are two main types:
- Ischemic Stroke: Caused by a blockage in an artery supplying blood to the brain (about 87% of all strokes).
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Caused by a ruptured blood vessel leading to bleeding in the brain.
Major Causes of Stroke:
- High Blood Pressure: The leading risk factor for both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): An irregular heartbeat that can cause blood clots in the heart, which may travel to the brain.
- Diabetes: Increases risk by damaging blood vessels.
- High Cholesterol: Contributes to plaque buildup and arterial blockages.
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and increases clot risk.
- Family History and Age: Risk increases with age and genetics.
Heart Attack vs Stroke: Key Differences
| Feature | Heart Attack | Stroke |
|---|---|---|
| Affected Organ | Heart | Brain |
| Main Cause | Blockage in coronary arteries | Blockage or rupture in brain arteries |
| Symptoms | Chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea | Face drooping, arm weakness, speech trouble |
| Onset | Gradual or sudden | Usually sudden |
| Immediate Risk | Heart muscle damage, cardiac arrest | Brain damage, paralysis, speech issues |
Prevention Strategies for Both Conditions
While the causes may differ slightly, the preventive steps for heart attacks and strokes often overlap.
1. Control Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a major risk factor for both conditions. Monitor your blood pressure regularly and take prescribed medications as directed.
2. Maintain Healthy Cholesterol Levels
Reduce intake of saturated fats and increase consumption of fiber-rich foods. Statins may be prescribed if levels are high.
3. Manage Diabetes
Keep blood sugar levels under control through medication, diet, and exercise.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking cessation significantly lowers your risk. Seek medical help if needed.
5. Exercise Regularly
At least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week helps maintain a healthy heart and vascular system.
6. Eat a Balanced Diet
The Mediterranean or DASH diets are especially beneficial. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
7. Limit Alcohol Intake
Excessive drinking increases blood pressure and can lead to both heart and brain issues.
8. Routine Check-ups
Annual physicals help detect issues early, especially in people with family history or other risk factors.
Conclusion
Heart attacks and strokes are serious medical emergencies that share some risk factors but differ in cause, symptoms, and treatment. Understanding these differences—and acting on the shared risk factors—can save lives. Preventive healthcare, lifestyle changes, and staying informed are essential steps toward reducing your risk.
References
- Benjamin, E. J., et al. (2019). Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation, 139(10), e56–e528. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659
- World Health Organization. (2023). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2022). Stroke Facts. https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/facts.htm
- American Heart Association. (2023). Heart Attack Symptoms, Risk, and Recovery. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2023). High Blood Pressure. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/high-blood-pressure
Read Also: 108 Names of Lord Shiva: Meaning, Significance, and Use in Spiritual Practice