Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Lunar eclipses have fascinated humans for centuries, inspiring myths, scientific discoveries, and cultural traditions. They remain among the most widely observed celestial events worldwide.
A lunar eclipse is one of the most fascinating celestial events that captures the attention of skywatchers across the globe. Unlike solar eclipses, which are visible only from specific regions, a lunar eclipse can be observed from anywhere on Earth where the Moon is above the horizon. But what exactly is a lunar eclipse, why does it happen, what are its different types, and why does the Moon appear red during certain eclipses? Let’s explore in detail.
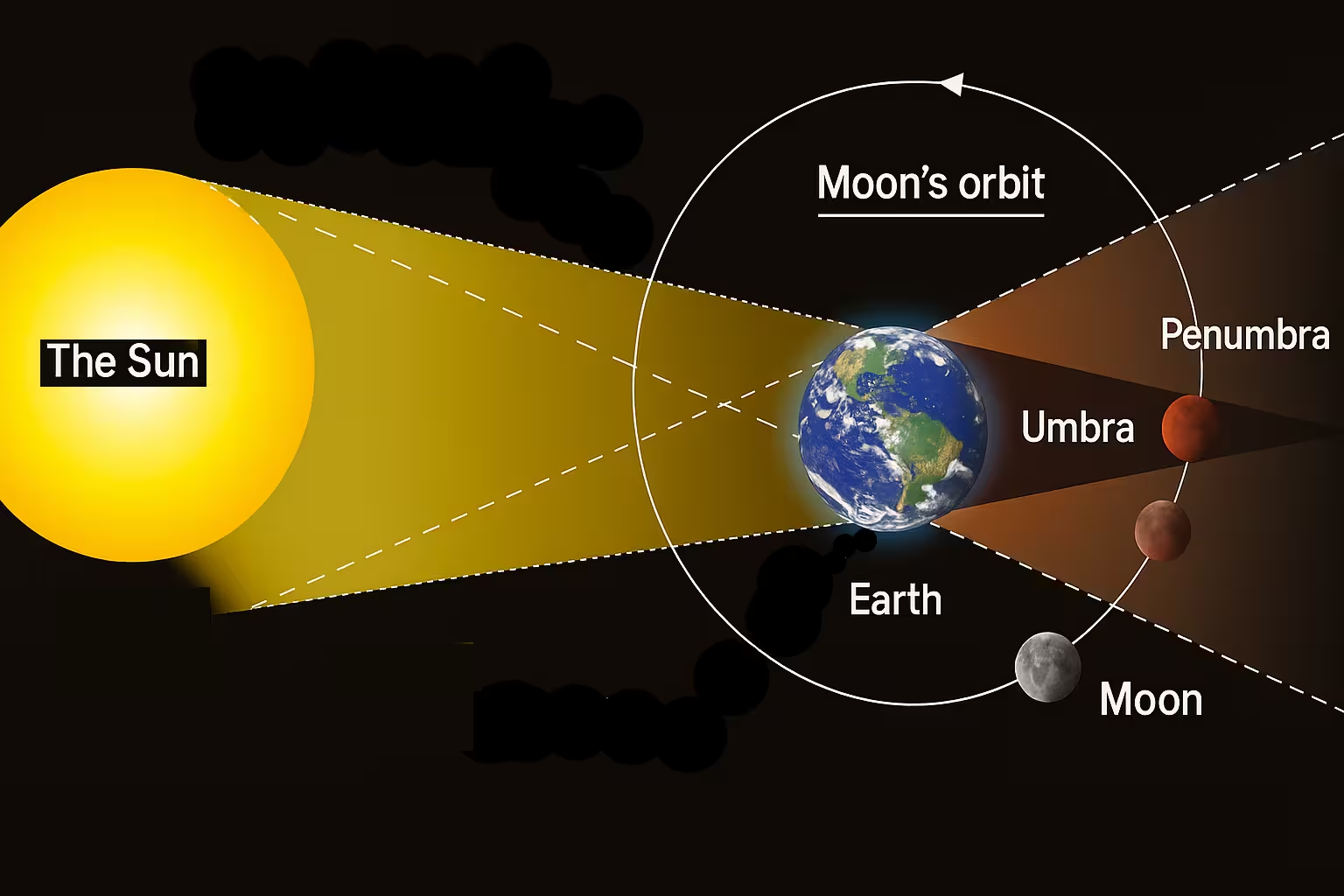
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth comes directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting its shadow on the Moon. This alignment causes the Sun’s light to be blocked from reaching the Moon, resulting in a partial or complete darkening of the lunar surface.
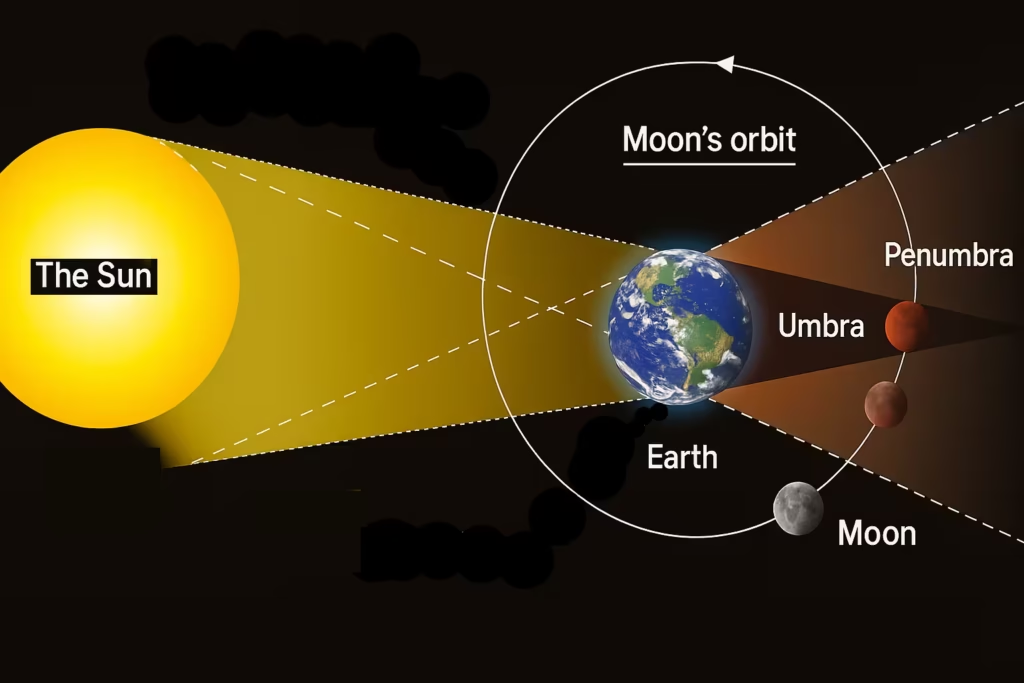
There are three main celestial bodies involved:
A lunar eclipse happens only during a full moon when the Sun, Earth, and Moon align in a straight line. However, not every full moon results in an eclipse. This is because the Moon’s orbit is slightly tilted (about 5 degrees) relative to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. An eclipse occurs only when the alignment happens near one of the orbital intersection points, known as nodes.
Not all lunar eclipses look the same. Each type offers a different visual experience and scientific significance. There are three primary types, but each can be further understood in terms of how much of the Earth’s shadow is involved, how noticeable the eclipse becomes, and how it is perceived culturally and historically.
In a penumbral lunar eclipse, the Moon passes through the Earth’s penumbra — the outer part of the shadow. This type of eclipse is subtle, and the dimming is often difficult to notice with the naked eye. Sometimes, careful observation or photography is needed to detect the faint shading. Because of its mild effect, penumbral eclipses are more common but also less dramatic. They can, however, last longer than partial or total eclipses, sometimes spanning over four hours, making them interesting for those studying the gradual shift in brightness.
A partial lunar eclipse occurs when only a portion of the Moon enters Earth’s umbra (the darkest part of the shadow). This causes a clear dark “bite” to appear on the Moon’s surface. Depending on how much of the Moon enters the umbra, the darkened area can cover a small fraction or almost the entire lunar disk. Partial eclipses are easier to notice than penumbral ones and often attract casual skywatchers. They also give scientists valuable opportunities to study the Earth’s shadow size and the effect of Earth’s atmosphere on sunlight bending around the planet.
A total lunar eclipse happens when the entire Moon passes through Earth’s umbra. During this time, the Moon takes on a reddish hue, which is why it is often called a “Blood Moon.” Total eclipses are considered the most spectacular type because of the dramatic transformation of the lunar surface. Depending on atmospheric conditions, the color can range from bright orange to deep red or even a darker brownish shade. Total eclipses may last for over an hour in their total phase, with the entire sequence of penumbral, partial, and total stages extending for several hours. For ancient civilizations, total lunar eclipses often carried mystical meanings, sometimes seen as omens, while today they provide exciting opportunities for photography and cultural celebrations.
Read Also : Lunar Eclipse of September 2025: Date, Time, Visibility in India | Lunar Eclipse 2025: When, Where, and How to See the Celestial Event
The Moon appears red during a total lunar eclipse due to a phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering. When sunlight passes through Earth’s atmosphere, shorter wavelengths (blue light) are scattered, while longer wavelengths (red light) bend and pass through. This red light is refracted onto the Moon’s surface, making it glow with a coppery-red color.
This effect is similar to why the sky looks red during sunrise and sunset.
From a scientific perspective, lunar eclipses have no direct impact on human health. They are purely astronomical events and do not emit harmful radiation. However, in astrology and cultural traditions, eclipses hold symbolic significance. Many cultures associate them with transformation, new beginnings, or cautionary periods. Practices such as fasting, meditation, and refraining from certain activities are observed in some traditions during eclipses.
Every lunar eclipse, whether penumbral, partial, or total, offers a unique view of the cosmic dance between the Sun, Earth, and Moon. For observers, it is not only a chance to witness astronomy in action but also an opportunity to connect with cultural traditions and the mysteries of the universe. Watching the Moon slowly transform in the night sky remains a powerful reminder of our place in the cosmos.